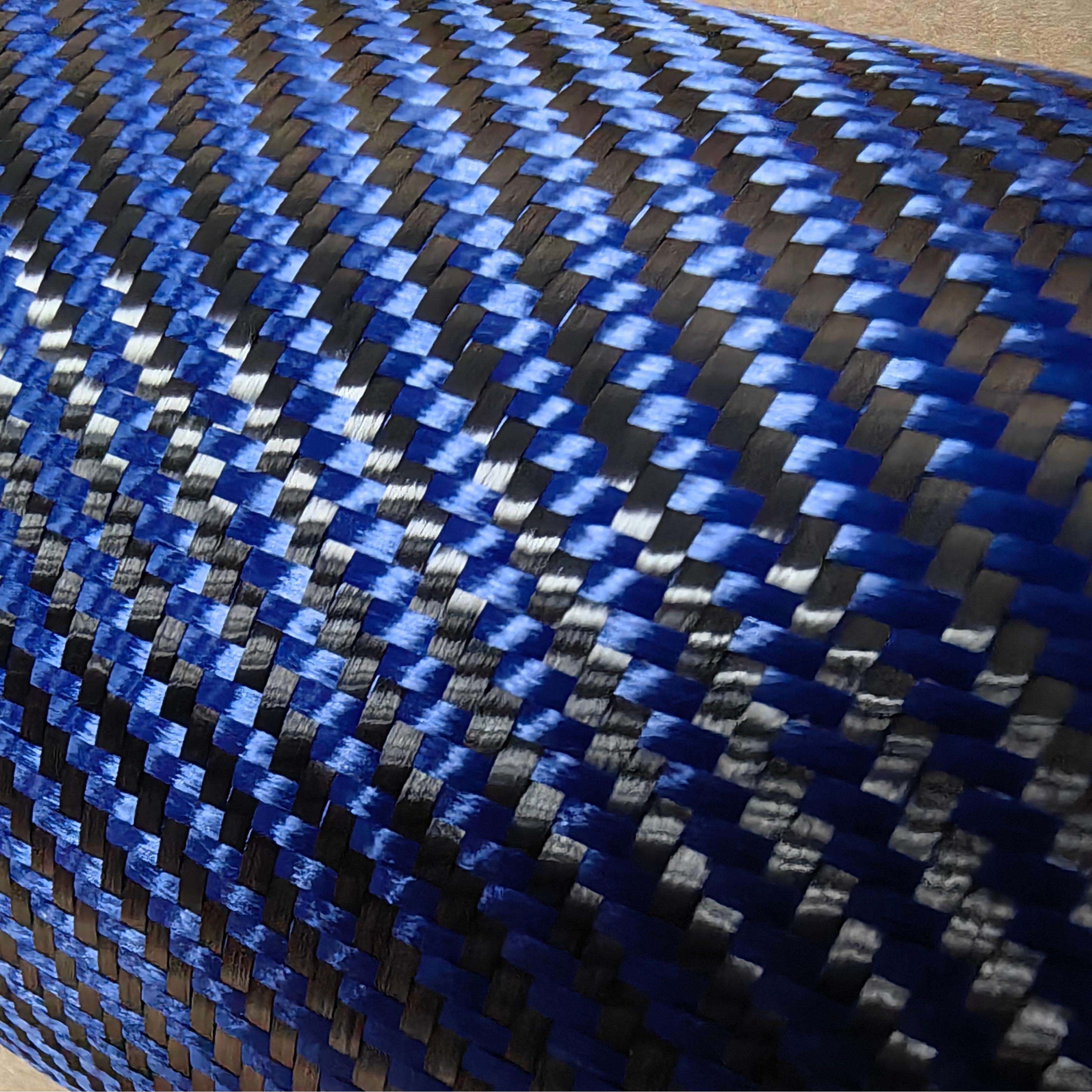
הפיתוח של חומרים מתקדמים מרוכבים מהפכן תעשיות רבות, החל מתעשיית התעופה והחלל ועד לייצור תעשייתי של רכב. בין התרומות המהותיות הללו, קומפוזיטים היברידיים של פחמן וקייבלר מייצגים קפיצת מדרגה משמעותית במדעי החומרים, המשלבים את יחס העוצמה-למשקל האיכותי של סיבי הפחמן עם התכונות הנפלאות של סיבי הקיאבר (aramid) של קייבלר בבלימת מכה. שילוב זה יוצר אפקט סינרגטי שעושה עיקרייה למגבלות של כל חומר בפני עצמו, תוך הגברה של היתרונות הצברים שלהם. הבנת אופן פעולתם המשותפת של חומרים אלו מספקת תובנות חשובות מהנדסים ויצרנים המחפשים פתרונות ביצועים אופטימליים ביישומים דרמטיים.
הבנת התכונות הבסיסיות של קומפוזיטים היברידיים
מאפייני סיבי הפחמן והיתרונות בביצועים
חומר סיבי פחמן מציג עוצמת משיכה יוצאת דופן ותכונות קשיחות שהופכות אותו לבלתי נזיל ביישומים מבניים הדורשים מינימום של עלות במשקל. לסיבים אלו יש מודולוס אלסטיות גבוה, שמתנודד בדרך כלל בין 200 ל-800 GPa, בצפיפות נמוכה בהשוואה לחומרים מתכתיים מסורתיים. המבנה הגבישי של אטומי הפחמן המסודרים בתבניות שובריות מספק חוזק כיווני יוצא דופן תוך שמירה על מאפיינים של מסה יחסית נמוכה. תכונות אלו הופכות את סיבי הפחמן לשימושיים במיוחד ביישומים שבהם שלמות מבנית תחת עומסי משיכה היא עיקרית.
תהליך הייצור של סיבי פחמן כרוך בפירוליזה מבוקרת של חומרי קדם אורגניים, בדרך כלל פוליאקרילוניטריל או תרכובות מבוססות זפת. תהליך זה יוצר שרשראות פחמן בעלות אוריינטציה גבוהה התורמות לתכונות המכניות יוצאות הדופן של החומר. עם זאת, חומרים מרוכבים מסיבי פחמן באופן מסורתי מציגים מאפייני כשל שבירים, במיוחד בתנאי עומס פגיעה, אשר יכולים להגביל את עמידותם. שימוש בסביבות שבהן צפויות עומסי הלם פתאומיים.
תכונות סיבי קברל ארמיד ועמידות במכה
סיבי קבלר ארמיד מפגינים עמידות יוצאת דופן ויכולת ספיגת אנרגיה שמשלימות את התכונות המבניות של חומרי פיברגלאס. סיבים סינטטיים אלו מציגים עמידות יוצאת דופן בפני תקיפה וחדירה בליסטית, מה שהופך אותם למרכיבים חיוניים ביישומים מגינים. המבנה המולקולרי של פולימרים ארמיד כולל טבעות אромטיות קשיחות המחוברות באמצעות קשרי אמיד, ויוצר מולקולות במחרוזת ארוכה שמתנגדות להימתחות ומספקות תכונות ספיגה מمتازות של אנרגיה בתנאי עומס דינמיים.
התכונות הוויסקו-אלסטיות של סיבי קברלמאפשרות להם לספוג כמויות גדולות של אנרגיה קינטית באמצעות מנגנוני עיוות שמונעים מצבים של כשל קטסטרופלי. בניגוד לסרן, שנוטה להיכשל בצורה שבירה, קברל מציג מאפייני כשל תדרוגיים המאפשרים המשך יכולת נשיאת עומס גם לאחר שנזק ראשוני התרחש. תכונה זו הופכת את סיבי הארמיד לבעלי ערך מיוחד ביישומים הדורשים סובלנות לנזק ועקרונות עיצוב בטוחי כשל.

מנגנוני היברידיזציה ואפקטים סינרגטיים
ארכיטקטורת סיבים ותצורת שכבות
הסדר האסטרטגי של סיבי פחמן וקברלאר בתוך מבנים מרוכבים היברידיים יוצר הזדמנויות לביצוע מיטוב של ביצועים מכניים באמצעות שיקול זהיר של רצף השכבות וכיוון הסיבים. היברידיזציה בין שכבות כוללת החלפה של שכבות של פabricות פחמן וקברלאר, בעוד שהיברידיזציה בתוך שכבה משלבת שני סוגי סיבים בתוך שכבות פabric יחידות. כל גישה מציעה יתרונות מובחנים בהתאם לדרישות הביצועים הספציפיות ולתנאי העומס הצפויים ביישומים בשירות.
שברית הנפח של הסיבים ודפוסי ההתפלגות משפיעים באופן משמעותי על התכונות המכניות המתקבלות פחמן קבר קומפוזיטים היברידיים. תצורות אופטימליות כוללות בדרך כלל מיקום אסטרטגי של שכבות סיבי פחמן כדי למקסם את הקשיחות המבנית, תוך מקצת שכבות קבלר כדי לאפשר ספיגת אנרגיה ויכולת סיבולת נזק. גישה ארכיטקטונית זו מאפשרת לעצבים להתאים את תכונות הקומפוזיט לצרכים ייחודיים של היישום, תוך שמירה על אפשרות ייצור.
שילוב מטריצה ואופטימיזציה של הממשק
מערכת המטריצה הפולימרית ממלאה תפקיד מרכזי בהעברת מאמצים בין סוגי סיבים שונים ובהבטחת יHAS שימוש בתכונות האינherent של כל חומר. מערכות רזין אפוקסי משמשות לרוב כחומרים מטריציים בזכות תכונות הדבקה מצוינות שלהן עם סיבי פחמן וקבלר. יש צורך באופטימיזציה זהירה של הממשק בין הסיבים למטריצה כדי להשיג יעילות מכנית מרבית, תוך מניעה של כשל מוקדם במפגש בין סיבים למטריצה.
עיבוד שטח וסוכרים כימיים משפרים את חוזק הקשירה בין סוגי סיבים שונים וחומר המטריצה שמקיף אותם. שינויי הכימיה האלה משפרים את יעילות העברת העומס ומצמצמים את הסיכון לכישלון בשל עיבוי, מה שעלול לפגוע בביצועים הכוללים של החומר המורכב.
מנגנוני שיפור התנגדות להשפעה
נתיבי ספיגת ואיבוד אנרגיה
ההתנגדות העדיפה של תערובות פחמן קווילר לאפקטים מכאניים נובעת ממכניזמים מרובים של ספיגת אנרגיה הפועלים בו-זמנית במהלך אירועים של פגיעה. שכבות פיברגלасс מספקות קשיחות ראשונית שמפיצה את עומסי הפגיעה על פני שטחים גדולים יותר, בעוד שכבות קווילר סופגות אנרגיה קינטית באמצעות התארכות הסיבים ועיוות המטריצה. התנהגות דואלית זו יוצרת אפקט סינרגטי שבו כושר ספיגת האנרגיה הכולל עולה על זה של כל חומר בנפרד.
התפתחות הנזק בהרכבות מערביות עוקבת אחרי דפוסים צפויים המאפשרים מצבי כשל מבוקרים תחת עומסי מכה. נזק ראשוני מתרחש בדרך כלל בצורת סדקים במחומר ובהתנתקות סיב-מחומר, ולאחר מכן התפרקות הדרגתית של הסיבים בשכבות הפחמן והרחקת סיבים נרחבת באזורים של קבלר. תהליך הכשל הסדרתי מאריך את משך הזמן שבו נ hấpנת אנרגיית המכה, מפחית ריכוזי מתח שיא ומונע קריסה מבנית קטסטרופלית.
סבילות לנזק וביצועים לאחר מכה
מבנים מתקופים היברידיים מציגים מאפייני סובלנות נזק יוצאי דופן המאפשרים המשך פעולה גם לאחר אירועים משמעותיים של פגיעה. נוכחותה של סיבי קווולר תורמת לאכיפת התפשטות נזק על ידי אספקת מנגנוני חיבור שומרים ngăn את הגידול המהיר של סדקים דרך שכבות סיבי הפחמן. יכולת אכיפת הנזק הזו היא ערך מיוחד ביישומים קריטיים לבטיחות, שבהם יש לשמור על שלמות המבנית גם לאחר נזק עקב פגיעה.
חוזק ללחיצה לאחר פגיעה מייצג לרוב שיקול עיצוב קריטי עבור מבנים מתקופים שנחשפים לעומס פגיעה. קומפוזיטים היברידיים של פחמן וקוולר מציגים ביצועי לחיצה-אחרי-פגיעה טובים יותר בהשוואה למצעי סיבי פחמן מלאים, בזכות הסבילות הגבוהה יותר לנזק שמספקות החיזוקים מסיבי הארמיד. יכולת חוזק שיורית משופרת זו מאפשרת עיצוב מבניות יעיל יותר עם מקדמי בטיחות מופחתים, תוך שמירה על רמות אמינות מקובלות.
נושאי ייצור ובקרת איכות
פרמטרים של עיבוד וتقنيות ייצור
ייצור מוצלח של קומפוזיטים היברידיים מפחמן וקייבלר דורש תשומת לב מדויקת לפרמטרי עיבוד שמתאימים את התכונות התרמיות והמכניות השונות של חומרי הרכיב. יש לדייק את פרופילי טמפרטורת העיבוד כדי להבטיח פולימריזציה מלאה של הרזין, תוך מניעה של דדגרדציה תרמית של סיבי הארמיד, אשר לרוב מציגים יציבות תרמית נמוכה בהשוואה לסיבי הפחמן. יש ליישם לחץ במהלך הקונסולידציה בכדי לאלם חללים, תוך הימנעות מדחיסה מוגזמת שעלולה לפגוע במבנה הסיבים.
טכניקות ההכנה של חלקי הפורם משפיעות על האיכות הסופית ומאפייני הביצועים של מבני הקומפוזיט ההיברידיים. טיפול נכון בבדי קווילר מחייב שימוש בכלים וטכניקות חיתוך מיוחדות כדי למנוע קריעה ולשמור על סובלנות ממדית מדויקת. יש לשלוט בזהירות בתהליכי ההטמעה של השכבות, כדי להבטיח כיוון סיבים נכון ולמנוע התקفات או גשרים שעלולים ליצור אזורים עשירים ברזין או ריכוזי מתח ברכיב הסופי.
פרוטוקולים לאבטחת איכות ולבדיקות
תכניות בקרת איכות מקיפות למרכبات היברידיות של פחמן וקייבלר כוללות טכניקות להערכה מרסיס וללא הרס כדי לאמת את תכונות החומר ולזהות פגמים בייצור. שיטות בדיקה אולטרסוניות מזוהות באופן יעיל התנתקויות, חללים ופערים פנימיים אחרים שעלולים לפגוע בביצועים המבניים. פרוטוקולי בדיקת מכה, הכוללים הערכות של נפילת משקל ומכה בליסטית, מאששים את תכונות ההתנגדות לכ удар שהן הצדקה לשימוש בבנייה היברידית.
לאפיון תכונות מכניות נדרשים שיטות בדיקה מיוחדות שמשלבות את אופני הכשל הייחודיים של חומרי ההיבריד הקומפוזיטיים. יש לכייל פרוטוקולי בדיקה להורדה, לחיצה ולחיצות כדי ליהנות מאפייני הכשל ההדרגתיים הטיפוסיים לחומרים מרוכבים של פחמן-كيفלר. הערכות עמידות ארוכות טווח, הכוללות בדיקות דליפה ומחקרים של חשיפה לסביבה, מספקות נתונים חיוניים להגדרת רמות עיצוב וחיזויי משך חיים בשירות.
יישומים ותפעול בתעשייה
יישומים באווירונאוטיקה ובהגנה
תעשיית התעופה והחלל אימצה שילובי קרבון-קווולר לApplications הדורשים עמידות יוצאת דופן בפני מכה בשילוב עם יעילות מבנית קלה. רכיבי כלי טיס שנחשפים לסיכון נזק מאירוסים, כגון קצוות קידמיים של כנפיים וגרבילים של מנועים, נהנים בצורה משמעותית מייכולת הספיגת האנרגיה המשופרת של בנייה משולבת. יישומים בכלי טיס צבאיים מנצלים את תכונות ההתנגדות הבליסטית של קווולר בשילוב עם היעילות המבנית של סיבי פחמן, כדי ליצור מבנים מגינים עם עונש משקל מינימלי.
בניה של להטות רוטור של מסוקים מייצגת תחום יישום משמעותי נוסף, שבו תכונות כיבוי הרטיטים של קברל משלבות את דרישות הקשיחות שמספק חיזוק בפיברגל. הבניה ההיברידית מאפשרת עיצוב להטות שמתגנות בפני כשל עייפות, תוך שמירה על היעילות האירודינמית החיונית לביצוע טיסה אופטימלי. יישומים אלו מדגימים את היתרונות הפרקטיים של שילוב חומרים בסביבות פעילות קשות.
תעשיית הרכב ותחבורה
יצרני רכב משלבים ביתר שאת קומפוזיטים היברידיים של פחמן-קвлר ברכיבים מבניים קריטיים לבטיחות, שבהם בליעת אנרגיית התנגשות היא עיקרון בסיסי. דפנות דלתות, עמודים וחיזוקי שלד משתמשים בבנייה היברידית כדי לעמוד בתקנות בטיחות קפדניות תוך fördern של מטרות הפחתת משקל כללית של הרכב. עמידות המכה המשופרת של הקומפוזיטים ההיברידיים מאפשרת חתכים מבניים דקים יותר בהשוואה לחומרים מסורתיים, ופותחת הזדמנויות לשיפור יעילות אריזה וגמישות בעיצוב.
יישומים אוטומotive בעלי ביצועים גבוהים, כולל תחומי המוטוספורט והכלי רכב הרשויים, משתמשים בחומרי גלם קרבון-קברלאר בפנלים של הגוף ובקomponents אירודינמיים שחייבים לעמוד בפני נזק מפגיעה של חפצים זעירים תוך שמירה על שלמות המבנית. מאפייני סיבולת הנזק הגבוהים של הבנייה ההיברידית מקטינים את דרישות התפעול ומארכים את חיי השרות של הרכיבים, ומספקים יתרונות כלכליים שמפצלים את עלות החומר ההתחלתית הגבוהה יותר.
פיתוחים עתידיים וכיווני מחקר
טכנולוגיות פיבר מתקדמות וחדשנות בחומרים
מחקר מתמשך בחיבורים של פחמן קווילר מתמקד בפיתוח טיפולים מתקדמים בפני השטח של סיבים ובטכניקות היברידיות חדשות שמשפרות עוד יותר את יכולת ההתנגדות להשפעה. יישומים של ננוטכנולוגיה, הכוללים אינטגרציה של ננו צינורות פחמן ושדרוג גרפן, מציגים תקווה ליצירת חומרים היברידיים דור חדש עם מאפיינים של ביצועים חסרי תקדים. התפתחויות אלו עשויות לאפשר לחומרים היברידיים להשיג רמות עמידות להשפעה שהושגו בעבר רק באמצעות חומרים מסורתיים כבדים בהרבה.
שילוב של חומרים חכמים מייצג חזית נוספת בפיתוח קומפוזיטים היברידיים, עם חיישנים משובצים ויכולות ריפוי עצמי שנחקרים ליישומים עתידיים. טכנולוגיות אלו עשויות לאפשר ניטור בזמן אמת של בריאות המבנית ושיקום אוטומטי של נזקים מינוריים, הארכת תוחלת חיים והפחתת דרישות התפעול והתחזוקה. שילוב של עמידות מוגברת בפני תקלות עם התנהגות חכמה של החומר עלולה להפוך את היישומים בתשתיות קריטיות ומערכות תחבורה.
האצת תהליכי ייצור
מפתחים טכניקות ייצור מתקדמות, כולל שילוב סיבים אוטומטי וחומרים תוספים, כדי לשפר את היחס בין עלות לאיכות וביצועים בהשגת ייצור של תערובות פחמן-קפלר. תהליכים אלו מאפשרים שליטה מדויקת יותר בכיוון ובהפצה של הסיבים, מה שיכול לחשוף יכולות ביצועים חדשות תוך הפחתת עלויות הייצור. ייצור תוספי עם סיבים מתמשכים מציג פוטנציאל מיוחד ליצירת צורות גאומטריות מורכבות עם מבני סיבים מותאמים במיוחד לתנאי עומס ספציפיים.
שקולות של מחזור וקיימות מובילים מחקר בחומרי מטריצה מבוססי ביולוגיה ובטכניקות עיבוד בסוף החיים למרכبات היברידיות. התפתחויות אלו עונות על דאגות סביבתיות תוך שמירה על היתרונות בביצועים שמפצים את מתקבצי הפחמן-קברל לאטרקטיביים ליישומים קפדניים. תהליכי ייצור בר-קיימא יכולים להרחיב באופן משמעותי את אימוץ השוק של מתקבצי היברידיות בתחומים שונים.
שאלות נפוצות
מה גורם למרכבי פחמן-קברל ההיברידיים להיות עמידים יותר בפני פגיעה לעומת חומרי סיבי פחמן טהורים
קומפוזיטים היברידיים של פחמן וקברלור משיגים עמידות מרשימה בפני תקלים הודות לתכונות המשלימות של שני סוגי הסיבים. בעוד שסיבי הפחמן מספקים קשיחות מבנית ועוצמה, הקברלור תורם יכולת יוצאת דופן לספיגת אנרגיה וסובלנות לפגמים. הבנייה ההיברידית מאפשרת לפעולות כשל מרובות לפעול בו זמנית, ובכך מאריכה את הזמן שבו נספגת האנרגיה הנגרמת מהפגיעה ומונעת מצבים של כשל חמור ושבירה אופיינית של קומפוזיטי פחמן טהורים.
איך שונה תהליך הייצור של קומפוזיטים היברידיים לעומת קומפוזיטים בעלי סיב אחד
ייצור תערובות פחמן קווילר מצריך שיקול דעת לגבי התכונות התרמיות והמכניות השונות של חומרי הבנייה. טמפרטורות עיבוד חייבות להתחשב בהיציבות התרמית הנמוכה של סיבי קווילר, תוך וידוא של עמידה מלאה של הרזין. סדרי ההרכבה של השכבות דורשים בקרת דיוק כדי למקסם את הביצועים המכניים, וטכניקות טיפול מיוחדות נדרשות כדי למנוע נזק לסיבי הארמיד בתהליכי הייצור.
אילו הן האפליקציות העיקריות בהן תערובות פחמן-קווילר מספקות את העניין הגדול ביותר
קומפוזיטים היברידיים של פחמן וקברלאר מצטיינים ביישומים הדורשים עמידות גבוהה בפני מכה בשילוב עם יעילות מבנית קלה. יישומים עיקריים כוללים רכיבים באווירונאוטיקה שנחשפים לנזק אפשרי מאפקט התנגשות בציפור, מבני בטיחות ברכב להספגות אנרגיית התנגשות, מערכות הגנה בליסטית, וציוד ספורט הדורש סובלנות נזק תחת מ ударיות בעלות אנרגיה גבוהה. יישומים אלה מנצלים את הצירוף הייחודי של קשיחות ועמידות שמבנה היברידי מספק.
איך קומפוזיטים היברידיים של פחמן וקברלאר משתווים במונחי עלות ויתרונות ביצועים
בעוד שקומפוזיטים היברידיים של פחמן וקברלאר עולים בדרך כלל יותר מאלטרנטיבות חד-סיביות, הם מציעים יתרונות ביצועיים משמעותיים העלולים להצדיק את ההשקעה. עמידות מוגברת בפני תקלות וסובלנות נזק מצמצמים את דרישות התפעול והתחזוקה ומאריכים את אורך החיים הפעוליים, מה שמספק יתרונות כלכליים לטווח הארוך. היכולת להשתמש בחתכים מבניים דקים יותר תוך שמירה על שולי הבטיחות יכולה אף היא לפצות על עלויות החומר באמצעות חיסכון במשקל ושיפור יעילות העיצוב ביישומים רבים.
תוכן העניינים
- הבנת התכונות הבסיסיות של קומפוזיטים היברידיים
- מנגנוני היברידיזציה ואפקטים סינרגטיים
- מנגנוני שיפור התנגדות להשפעה
- נושאי ייצור ובקרת איכות
- יישומים ותפעול בתעשייה
- פיתוחים עתידיים וכיווני מחקר
-
שאלות נפוצות
- מה גורם למרכבי פחמן-קברל ההיברידיים להיות עמידים יותר בפני פגיעה לעומת חומרי סיבי פחמן טהורים
- איך שונה תהליך הייצור של קומפוזיטים היברידיים לעומת קומפוזיטים בעלי סיב אחד
- אילו הן האפליקציות העיקריות בהן תערובות פחמן-קווילר מספקות את העניין הגדול ביותר
- איך קומפוזיטים היברידיים של פחמן וקברלאר משתווים במונחי עלות ויתרונות ביצועים